The year 2024 has witnessed a severe dengue fever epidemic in several countries, notably Honduras and Brazil, impacting public health significantly. According to the Ministry of Health of Honduras, there have been over 18,000 reported cases of dengue fever, resulting in at least 13 deaths since the beginning of the year. This has prompted the issuance of the highest level warning by the health authorities, emphasizing the critical nature of the situation.
Similarly, Brazil has faced a staggering rise in dengue fever cases, surpassing 5 million infections and recording approximately 3,000 deaths as of the latest reports from the Brazilian Ministry of Health. This marks a notable increase compared to previous years, highlighting the severity and rapid spread of the disease across the country.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has noted an alarming increase in dengue fever infections in 2024, affecting countries across Central and South America, as well as Southeast Asia. Factors such as climate change, prolonged rainy seasons, and higher temperatures have contributed to conducive conditions for mosquito breeding and dengue virus transmission.
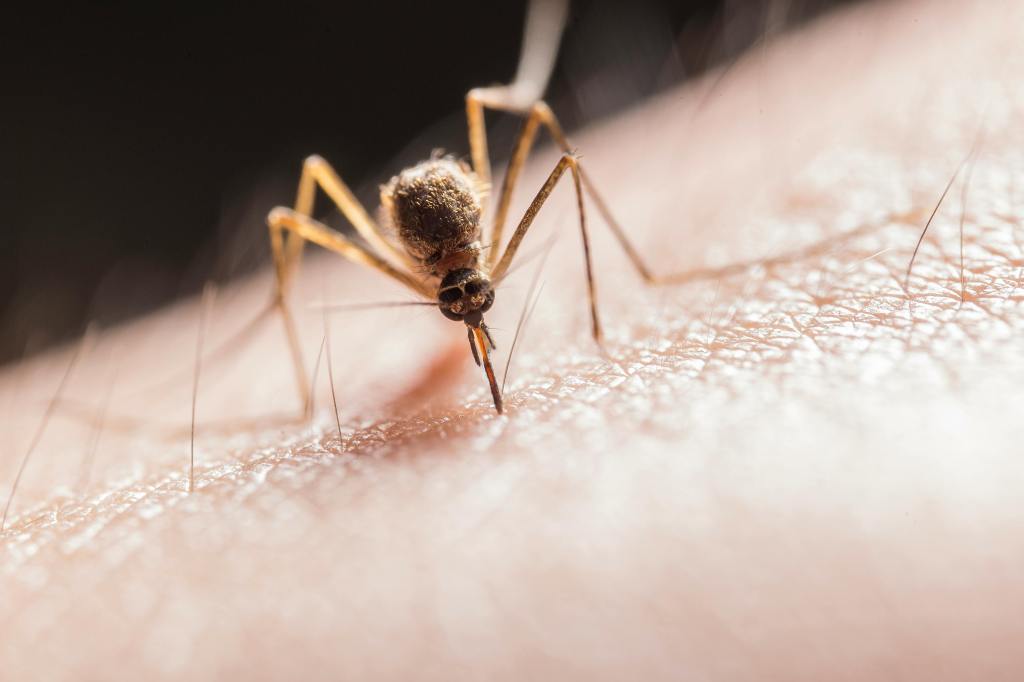
Dengue fever, caused by the dengue virus transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes, presents with symptoms including sudden high fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, and rash. There is currently no specific antiviral treatment for dengue fever, with management focusing on symptom relief and supportive care to prevent complications.

To mitigate the impact on public health sectors, efforts are underway in affected countries to establish temporary medical wards, conduct widespread insecticide spraying, and eliminate mosquito breeding sites. These measures are crucial for controlling the spread of the disease and providing timely medical assistance to affected individuals.
In conclusion, while dengue fever remains a significant health challenge globally, early detection, effective mosquito control measures, and prompt medical intervention are essential for managing outbreaks and reducing the burden on healthcare systems. Continued vigilance and proactive public health measures are necessary to combat this ongoing epidemic effectively.